
Vol. XXV, No. 13, December 2025
- Editor's corner
- The competitive challenge of immersive experience venues
- A missed opportunity for many location-based entertainment venues
- Netflix enters the location-based entertainment industry.
- Good interior design requires far more than architectural design
- The growing OOH market share for live sports
- Agritourism, significant competition for LBEs
A missed opportunity for many location-based entertainment venues
Many location-based entertainment venues (LBEs) now offer quality food. In fact, for some, including many social gaming centers, food and beverage is the majority of their revenues. Yet most LBEs continue to only offer on-premises dining.
The food and beverage offerings of most LBEs fall within the Fast Casual or Casual Dining restaurant segments:
- Fast Casual restaurants are a hybrid concept that bridges the gap between fast food/quick service (QSR) and casual dining, offering freshly prepared, customizable meals, often made to order, with ingredients perceived as higher quality and less processed than those in fast food, served up in a comfortable or even upscale ambiance and limited table service. The staff may deliver food to the table, but they do not offer full service. Prominent examples are Chipotle Mexican Grill, Panera Bread, Sweetgreen, and Shake Shack.
- Casual Dining restaurants are sit-down establishments characterized by a relaxed atmosphere, moderate pricing, full table service from waitstaff, and a broad, moderately priced menu that typically includes appetizers, main courses, desserts, and alcoholic drinks. Well-known Casual Dining chains include Olive Garden, Applebee's, Chili's, and Outback Steakhouse.
In the restaurant industry, excluding Fine Dining, a large share of sales now comes from off-premises channels, including drive-thru, curbside, to-go, and delivery.
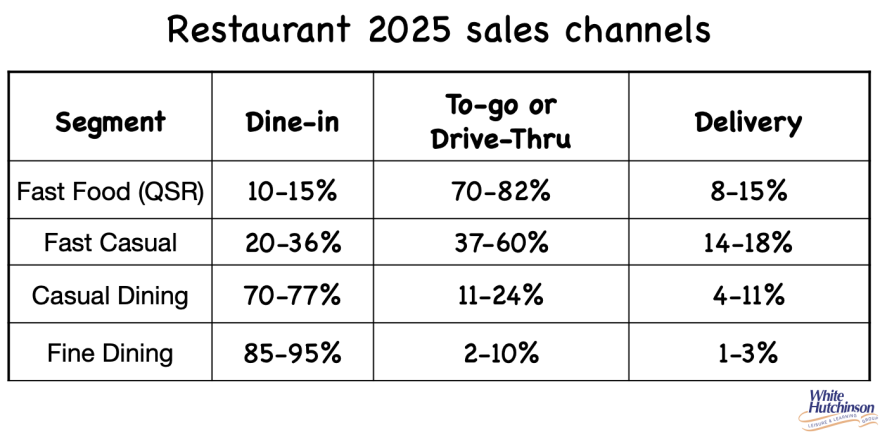
In 2025, approximately 47% of Americans purchased off-premises food (takeout or delivery) from Fast Casual restaurants at least once a week, while 34% did so from Casual Dining restaurants at least once a week. These percentages are even higher among Millennials, Gen Z, and urban residents, often topping 60% for fast casual and approaching 50% for casual dining, driven by strong preferences for convenience and mobile ordering.
Fast Casual and Casual Dining restaurants typically see off-premises sales grow after adding to-go and delivery options.
One advantage of adding delivery is that it can increase orders during non-peak dine-in hours. Lunch delivery extends later in the afternoon than dine-in, and the dinner delivery peak starts later than dine-in, with high volume extending much later, often up to 10 pm, especially on Fridays and Saturdays. Overall, adding delivery expands order volume to hours with lower dine-in demand, not only increasing daily sales but also improving kitchen production consistency.

A growing number of LBE chains now offer takeout and delivery, especially in urban and suburban markets:
- AMC Cinema Dine-In locations and similar dine-in theater chains in major markets partner with third-party platforms (such as DoorDash, GrubHub or Uber Eats) to deliver select menu items, including popcorn, snacks, and hot foods.
- Dave & Buster's offers delivery of their food menu - including wings, burgers, and shareables - via third-party apps in multiple cities, allowing customers to order for home consumption in addition to takeout.
- Bowling alleys: Chains like Bowlero now provide delivery for popular menu selections via partnerships with delivery services especially in larger metro areas
- Golf venues: Some venues (T-Shotz, Topgolf in select cities) offer third-party delivery through platforms for their restaurant-quality menus.
- Main Event has launched delivery in multiple states, especially Texas, Florida, and California, offering wings, pizza, and party platters.
- Chuck E. Cheese delivers pizza, wings, and family meals via third-party platforms in most urban and suburban locations
- Urban Air Adventure Park provides food delivery for birthday parties and off-site events in select markets.
- Andretti Indoor Karting & Games partners with delivery platforms for home delivery of menu offerings at some locations
The takeaway is that LBEs, where food accounts for a significant share of sales, can grow sales by offering to-go and delivery options through third-party delivery services.
Subscribe to monthly Leisure eNewsletter
Vol. XXV, No. 13, December 2025
- Editor's corner
- The competitive challenge of immersive experience venues
- A missed opportunity for many location-based entertainment venues
- Netflix enters the location-based entertainment industry.
- Good interior design requires far more than architectural design
- The growing OOH market share for live sports
- Agritourism, significant competition for LBEs


