
Vol. XXV, No. 10, September 2025
- Editor's corner
- The latest scoop on alcoholic consumption
- Participation in out-of-home activities
- Managing key performance indicators for profitable food and beverage
- Americans' evolving nightlife culture
- How real is virtual? Comparing the experience of a theme park dark ride with its VR counterpart
- Most popular alcoholic beverages
How real is virtual? Comparing the experience of a theme park dark ride with its VR counterpart
Virtual reality (VR) is transforming leisure and entertainment by providing a digital alternative to traditional, in-real-life physical experiences. A research study, published on June 16, 2025, in the Journal of Leisure Research, examined how closely a VR experience approximates its real-life counterpart and the role that social interactions play in this. The study compared the emotional responses during a physical dark ride and its VR counterpart at a theme park in Northwestern Europe.
A total of 145 participants experienced the ride in one of three conditions:
- the physical dark ride,
- the VR equivalent ride in isolation,
- the VR ride with social interaction.
Of the 145 participants, 47 rode the physical attraction, 46 rode the VR ride with social interaction, and 52 rode the VR ride without social interaction.
The dark ride attraction consisted of a 340-second experience that takes its visitors flying through a dream world of castles, forests, fairies, elves, and other elements and creatures related to fairy tales. Visitors are seated in small, open gondolas that hang on a transportation rail. The dark ride has a VR counterpart designed by the theme park for visitors with mobility restrictions who are unable to experience the physical ride due to safety reasons.
The VR experience replicates the physical ride as closely as possible, utilizing a carefully filmed virtual environment created with professional-grade equipment, including a stabilizer and cameras equipped with three types of 180° and 160° lenses. The filming process was performed in high resolution (8K), and the footage was recorded using filming techniques designed to accurately replicate the visual and spatial dynamics of the physical ride, with precise synchronization of visual elements.
In the VR social condition, participants used audio headsets equipped with headphones and microphones to verbally communicate simultaneously with their counterparts in the physical ride, allowing for real-time interaction throughout the experience. In contrast, participants in the VR plain condition experienced the virtual ride alone, without any communication or auditory connection to others.
Emotional responses were measured through real-time skin conductance and post-ride self-reports. Results indicate that the physical ride elicited stronger emotional responses, higher evaluations, and greater intentions to recommend and revisit. Additionally, the VR ride with social interaction was more arousing than the isolated VR ride and more closely resembled the physical experience.
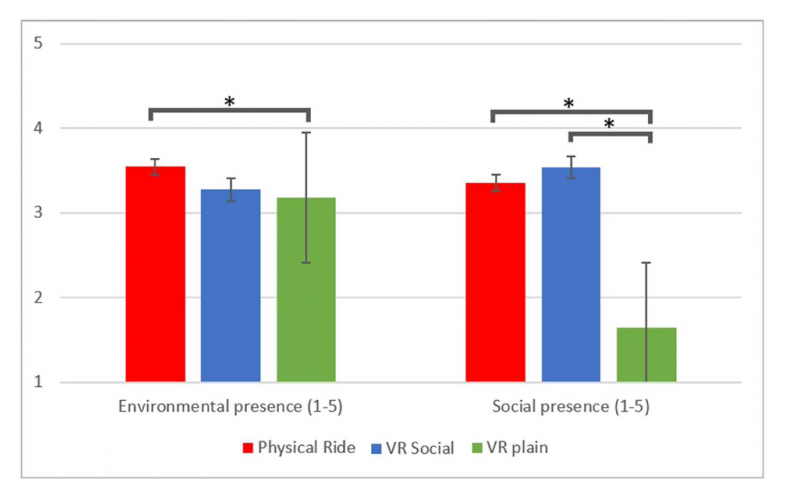
The self-reported environment and social presence of the three
ride conditions. Asterisks represent significant differences.
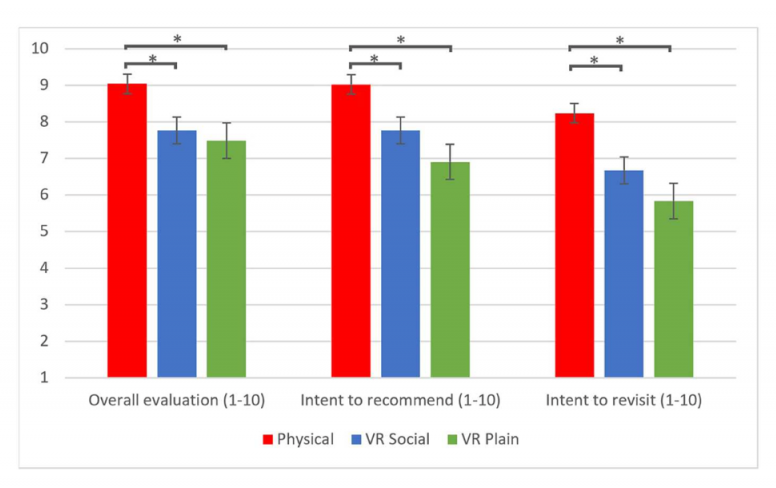
Experience outcome measures for the three conditions.
Asterisks represent significant differences.
The study found that while VR holds great potential and has advanced considerably in terms of being highly immersive and enjoyable, a notable gap still exists between a physical theme park dark ride and a virtual one. The study found that physical rides are better than virtual ones as they elicit stronger emotional responses, are assessed more positively, and are more likely to be recommended and revisited.
The findings highlight the importance of social interaction in intensifying the emotional impact of virtual experiences to make them closer to the physical experience. Other research has found that social interactions are very often the primary source of satisfaction and fulfillment in tourists' and entertainment venue visitors' activities.
The research has practical implications for VR developers and the leisure industry. First, identifying the key elements of physical experiences - such as motion - that elicit stronger emotional responses can guide the development of more effective virtual environments by ensuring these aspects are better replicated. Second, social interaction, a key driver of engagement in real-life leisure settings, is also crucial in enhancing virtual leisure experiences. Enabling social connections in virtual settings can help mitigate some of the disparities between physical and virtual experiences, opening up exciting possibilities for the leisure industry. To bridge the gap between VR and real-world experiences, VR designers should prioritize socially interactive features to create more engaging and emotionally fulfilling experiences.
Subscribe to monthly Leisure eNewsletter
Vol. XXV, No. 10, September 2025
- Editor's corner
- The latest scoop on alcoholic consumption
- Participation in out-of-home activities
- Managing key performance indicators for profitable food and beverage
- Americans' evolving nightlife culture
- How real is virtual? Comparing the experience of a theme park dark ride with its VR counterpart
- Most popular alcoholic beverages


